Key Takeaways
- Do not overestimate AI capabilities or set unrealistic expectations
- Implement proper governance and oversight over AI agents
- Beware the rise of shadow IT within your business units
- It's all about the data, data, and data
- Prioritize user experience alongside technological innovation
- Ensure sufficient AI guardrails against known and unknown risks
- Employ the right tool for the right job
- Continuously monitor and maintain your AI agents
The future of work is here, driven by innovations like agentic AI and autonomous AI agents. Companies—both big and small—are now making significant strides in harnessing the power of agentic process automation to transform their business operations. However, deploying AI agents effectively can be a tricky endeavor. Without careful planning and oversight, even the most promising AI initiatives can falter.
In this blog post, we’ll uncover eight critical pitfalls to avoid when deploying AI agents. By steering clear of these common mistakes, businesses can unlock the full potential of agentic automation while safeguarding against setbacks.
1. Overestimating AI Capabilities and Setting Unrealistic Expectations
AI agents are powerful, but they are not a silver bullet to all your business challenges. One of the most common pitfalls is assuming that AI can solve every problem instantly or autonomously, with minimal input. This leads to setting unrealistic goals, which can result in disappointment and disillusionment when outcomes fall short. For example, an AI agent designed for invoice reconciliation may excel at matching payments to invoices but could struggle with complex scenarios involving requiring institutional knowledge that are commonly undocumented.
To avoid this, establish clear, measurable objectives for your agentic AI deployment. Understand the limitations of your technology and communicate them to stakeholders to set achievable expectations. At the same time, understand that not all problems require an AI solution. For example, certain use cases involving rule-based tasks may be more suited for Robotic Process Automation solutions (see How to Select the Right Use Cases for Enterprise AI Agents).
“If the only tool you have is a hammer, you tend to see every problem as a nail.”
— Abraham Maslow
2. Lack of Governance or Oversight
An agentic workforce requires robust governance. Without oversight, AI agents may stray from organizational goals or even create unintended risks, such as non-compliance, biasness, and unethical decision-making. In the worst cases, a lack of oversight can lead to significant operational and reputational risks.

Avoid the pitfall: Establish governance frameworks that define roles, responsibilities, and accountability for your AI agents. Conduct regular audits and reviews to ensure alignment with business objectives and compliance standards.
3. Rise of Shadow IT
As AI agents gain popularity, employees or departments may deploy these tools without the IT department's knowledge. This "shadow IT" can lead to fragmented systems, data silos, and potential security vulnerabilities. This risk often arises when enterprises are slow to adopt and embrace emerging technologies. For example, according to research by Bain, enterprise use case adoption rates for generative AI are still relatively low, in spite of the fact that ChatGPT has reached mainstream consciousness with unprecedented speed.
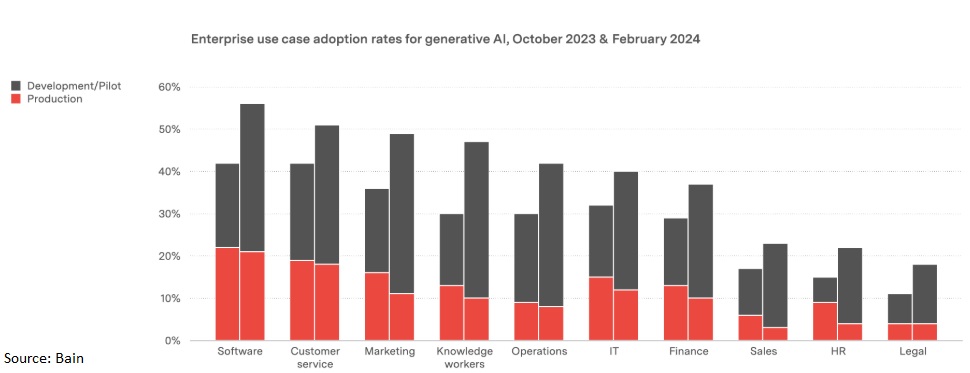
To mitigate this risk, it is vital to foster stronger collaboration between IT and business units. Create streamlined processes for deploying agentic solutions to maintain control and security while addressing business needs.
4. Underestimating the Importance of Quality Data
AI agents are only as good as the data they’re trained on. Poor data quality—whether it's incomplete, outdated, or biased—can lead to flawed decisions, inaccurate outputs, and diminished trust in the system. Without high-quality data, even the most advanced AI models can produce misleading insights or fail to deliver expected outcomes.

To mitigate this risk, prioritize establishing a comprehensive data governance framework. Ensure that your data is clean, accurate, and representative of real-world scenarios across diverse use cases. Regularly audit data sources for consistency and relevance, and implement processes to manage data integrity throughout its lifecycle. By doing so, your agentic AI initiatives will have the solid foundation needed to drive reliable and impactful results.
5. Poorly Designed User Experience (UX)
AI agents often interact with users and customers directly, making user experience a critical factor in the success of these deployments. A poorly designed experience can frustrate users, lead to disengagement, and tarnish your brand’s reputation. Common issues include confusing interfaces, limited functionality, or responses that lack empathy.
To quote some statistics on the important of customer experience (AI or not):
- 65% of all consumers find a positive experience with a brand to be more influential than great advertising
- 59% of all consumers feel companies have lost touch with the human element of customer experience.
- 32% of all customers would stop doing business with a brand they loved after one bad experience. In Latin America, 49% say they’d walk away from a brand after one bad experience.
- Consumers say they’re willing to spend 16 percent more to do business with companies that deliver excellent service
To avoid this pitfall, design intuitive, user-friendly interfaces that anticipate user needs and behaviors. Prioritize customer experience at every stage by integrating personalization and proactive support features. Continuously gather feedback through user testing and analytics, and iterate on your designs to ensure that your AI agents provide value, convenience, and satisfaction in every interaction.
6. Insufficient AI Guardrails
AI agents can hallucinate, become misaligned with business goals, or fail to comply with regulations. Without proper guardrails, these risks can escalate quickly and have serious consequences.

Avoid this pitfall by deploying safeguards to monitor AI behavior, detect anomalies, and prevent harmful outputs. This includes implementing bias detection tools, ethical AI frameworks, and automated compliance checks. Regular testing, validation, and alignment with ethical principles are critical to maintaining trust in your agentic AI solutions.
"The development of full artificial intelligence could spell the end of the human race."
— Professor Stephen Hawking
7. Inadequate Orchestration Between AI Agents, RPA Bots, and Human Experts
For agentic process automation to deliver optimal results, seamless collaboration between AI agents, RPA bots, and human experts is essential. Different tasks are best suited for different resource types—AI agents excel at decision-making and handling dynamic work, RPA bots automate repetitive, rule-based tasks efficiently, and human experts provide critical thinking and creativity. Without proper orchestration, assigning tasks to the wrong resource and not coordinating the outputs from the various parties can lead to inefficiencies, miscommunication, and costly errors. This disconnect can hinder process efficiency and slow down innovation.

To overcome this challenge, design integrated workflows that clearly define the roles and responsibilities of AI systems, automation tools, and human employees. Implement advanced orchestration platforms to automate task delegation, streamline communication, and coordinate handoffs between AI agents, RPA bots and human experts. Regular reviews and adjustments to these workflows will ensure continuous improvement and alignment with evolving business goals.
8. Neglecting Monitoring and Maintenance Post-Deployment
Deploying AI agents is not a one-time effort but an ongoing commitment. Neglecting continuous monitoring and proactive maintenance can lead to performance degradation, outdated functionalities, and increased vulnerabilities to emerging threats. Over time, even well-optimized AI agents can drift from their intended objectives, potentially causing inefficiencies and misaligned outcomes. As Henry Ford famously said, "The only thing worse than training your employees and having them leave is not training them and having them stay." Ditto for AI agents.
To mitigate these risks, implement a comprehensive monitoring framework that tracks AI performance metrics, detects anomalies, and ensures compliance with regulatory and ethical standards. Regular updates, retraining on fresh data, and adaptive maintenance practices are essential to keep autonomous agents efficient, accurate, and aligned with dynamic business goals. Additionally, incorporating feedback loops from users and stakeholders can help refine and improve AI performance over time, driving sustained value and innovation.
Final Thoughts
Deploying AI agents is a transformative journey, but it requires careful planning, oversight, and a commitment to continuous improvement. By avoiding these eight pitfalls, your organization can fully leverage agentic AI and build an agentic workforce poised to thrive in the future of work.
8 Key Pitfalls to Avoid When Deploying AI Agents