AI Agents FAQs
What are AI agents?
AI agents are intelligent software systems designed to perform complex, dynamic tasks autonomously. By utilizing advanced technologies such as Machine Learning, Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA), these agents can understand context, reason and plan tasks, perform actions, and make informed decisions in real-time. They are designed to work independently, while collaborating with other AI agents and human experts when required. By learning and reflecting on data and feedback, they are able to adapt to dynamic environments to achieve the desired objectives.
What are agentic workflows?
An agentic workflow is a dynamic, autonomous system where tasks and processes are managed and executed by intelligent AI agents. Unlike traditional workflows that reply on static business rules or pre-defined logic, agentic workflows are able to adapt in real-time to changing conditions. They achieve this through advanced capabilities such as leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for contextual understanding and reflection, usage of tools to execute actions, strategic planning and reasoning, and seamless multi-agent collaboration.
What is Agentic Process Automation?
Agentic Process Automation (APA) refers to the next evolution of automation, where intelligent AI agents autonomously manage and execute end-to-end business processes. Combining the capabilities of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) with advanced capabilities like Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) and Intelligent Document Processing (IDP), APA enables automation to go beyond repetitive, rules-based tasks. AI agents in APA can analyze data, make informed decisions, and adapt to variances and exceptions, ensuring seamless operation even in dynamic environments. By integrating with enterprise applications, and collaborating with other AI agents and humans expert when required, APA drives higher operational efficiency and effectiveness than traditional automation methods.
What are the differences between Generative AI and Agentic AI?
Generative AI and Agentic AI are related but distinct concepts within the field of artificial intelligence. The former is content-focused while the latter is action-oriented.
Generative AI refers to AI models such as Large Language Models (LLMs) that generate new content based on their training data. Today's state-of-the-art models are capable of generating high quality, multi-model content including text, programming code, images, audio, video, and more.
Agentic AI, on the other hand, consists of autonomous AI agents that can plan, make decisions, and interact with external systems to achieve specific goals, even in dynamic or unpredictable environments. These AI agents often incorporate Generative AI for reasoning and communication but also leverage reinforcement learning, APIs, and in some cases, Large Action Models (LAMs) to execute tasks.
What are RPA bots?
RPA bots are software bots that emulates a person executing manual, repetitive tasks. Just like a human, RPA bots are able to work with different applications and systems through the User Interface (UI), although increasingly, these bots are automating tasks via Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) as well.
What are the benefits of AI agents?
- Automates repetitive tasks, freeing up employees for high-value work
- Enhances efficiency by handling tasks at scale
- Provides real-time data insights for smarter decision-making
- Works seamlessly with existing systems and workflows
- Enables businesses to grow without proportional cost increases
- Improves accuracy, consistency, and compliance across operations
How much time does it take to deploy an AI agent?
With our tried-and-tested 4-step FastTrack Agent Onboarding© methodology, deploying an AI agent takes as little as 1-2 weeks.
What is the cost of an AI agent?
For pricing inquiries, please kindly contact our sales for more information.
What are some common mistakes when deploying AI agents?
Organizations often encounter these pitfalls when deploying AI agents:
- Overestimating AI capabilities and setting unrealistic expectations.
- Lack of governance or oversight over AI agents.
- The rise of shadow IT.
- Underestimating the importance of quality data.
- Poorly designed user experience, particularly in customer interactions.
- Insufficient AI guardrails against risks like hallucinations or non-compliance.
- Inadequate orchestration of work between AI agents, RPA bots, and human experts.
- Neglecting monitoring and maintenance of AI agents post-deployment.
- Inability to scale AI agents across the entire enterprise
What is Agent Programming Interface?
Unlike a traditional Application Programming Interface (API), an Agent Programming Interface (AgPI) is specifically designed to enable communication and collaboration among autonomous AI agents, particularly within multi-agent systems. It offers the tools and protocols needed for specialized agents to interact and cooperate seamlessly in dynamic, complex environments, working collectively toward shared objectives.
What is Service as a Software?
Service as a Software (SaaS) is an innovative model where intelligent, autonomous AI agents perform tasks traditionally handled by humans. Unlike conventional Software as a Service platforms that require on user intervention, this approach automates entire business processes, empowering talent-constrained businesses to leverage digital labor on demand for enhanced efficiency and scalability.
What does the workforce of the future look like?
The workforce of the future is a trifecta of AI agents, RPA bots, and human experts working together seamlessly. AI agents excel in intelligent decision-making and performing complex, dynamic work, RPA bots automate repetitive tasks with precision and reliability, and human experts provide strategic oversight and creativity. This hybrid approach enhances efficiency, effectiveness, and innovation in modern organizations.
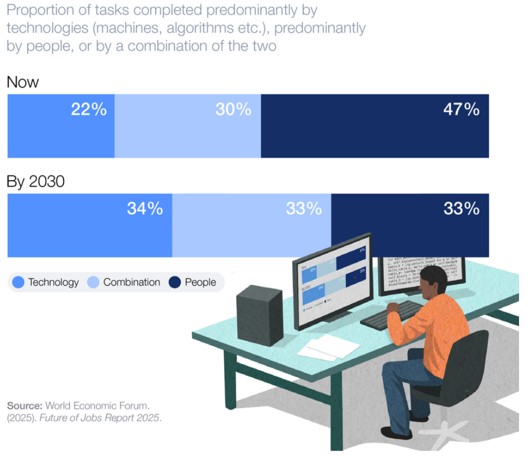
For example, in the Future of Jobs Report 2025, the World Economic Forum predicts that by 2030, as much as 33% of tasks will be completed by a combination of technologies (AI agents and RPA bots) and people.
What is Agentic IQ?
Agentic IQ is a measure of an organization's maturity, readiness, and capability in adopting and effectively integrating AI agents into its operations. It evaluates how well an organization combines AI-driven automation, such as AI agents and RPA bots, with human expertise to optimize business processes, enhance decision-making, and deliver improved customer and employee experiences. Organizations with high Agentic IQ exemplify a strategic approach to automation, leveraging a hybrid workforce where AI agents handle complex cognitive tasks, RPA bots manage repetitive processes, and human experts focus on strategy and innovation.
Common myths about AI agents
- Are AI agents here to replace humans? Not really. The ultimate goal of AI agents is to augment and assist humans rather than to replace them. The fundamental belief is that some work are best suited for AI agents and RPA bots, while others are more tailored for humans.
- Are AI agents only for large enterprises? Not true. The democratization of AI and automation technologies, coupled with the emergence of low-code and no-code tools, means that AI agents are highly accessible to organizations of all sizes. Your ingenuity is truly the only limits.
Three Laws of Agentic AI
- AI agents are designed to assist, augment, and empower humans, always prioritizing the safety, well-being, and advancement of humanity.
- Humans hold ultimate responsibility for the actions and outcomes of the AI agents they develop, deploy, or utilize, ensuring ethical and responsible use.
- AI agents must be consistently monitored, updated, and refined to maintain optimal performance, relevance, and alignment with evolving human values and goals.